- Published on
AI Agents vs Agentic AI: The Critical Distinction Explained
- Authors
- Name
- Parth Maniar
- @theteacoder
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence is evolving, and the buzz around AI Agents versus Agentic AI is growing louder. Yet many still mix up these two concepts. In this post, we'll break down the key differences, highlight real-world examples from companies like Waymo, Tesla, and Google, and explain why understanding these nuances is crucial for AI professionals, tech enthusiasts, and business leaders.
Imagine AI as a driver: traditional AI Agents are like GPS systems giving turn-by-turn instructions, while Agentic AI is akin to a self-driving car that makes autonomous decisions on the road. Let’s dive into this fascinating topic.
Defining AI Agents
AI Agents have been around for decades. They are designed to perform specific tasks with human input, following a set of instructions or rules. Think of them as specialized tools built for particular jobs.
Key Characteristics:
- Instruction Following: They perform tasks as directed (e.g., Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant).
- Human-in-the-Loop: They often require human prompts or oversight.
- Narrow Focus: Designed for well-defined, predictable tasks.
Real-World Examples:
- Waymo Self-Driving Cars: Operate based on pre-programmed rules and human-designed algorithms.
- Tesla’s Autopilot: Assists drivers by executing specific maneuvers while expecting human intervention in edge cases.
- Virtual Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant rely on instruction-based responses.

Understanding Agentic AI
Agentic AI takes things a step further. It is a system that not only follows instructions but also learns, adapts, and makes autonomous decisions. Agentic AI is designed to optimize its own performance, often involving multiple AI agents that work together.
Key Characteristics:
- High Autonomy: Operates with minimal human input.
- Learning and Adaptation: Adjusts its behavior based on feedback.
- Self-Evaluation: Incorporates judges and critics to refine decisions.
- Integrated Decision-Making: Orchestrates multiple agents to handle complex tasks.
Real-World Examples:
- Google DeepMind: Their systems often integrate several AI agents to solve complex problems, such as mastering games or optimizing data center efficiency.
- Autonomous Financial Trading Platforms: Some investment firms use agentic AI to manage portfolios by dynamically adapting strategies without constant human oversight.
- Agentic Customer Service Systems: Companies like Beta Corp deploy multi-agent AI systems that autonomously manage customer inquiries, gather data, and optimize responses in real time.
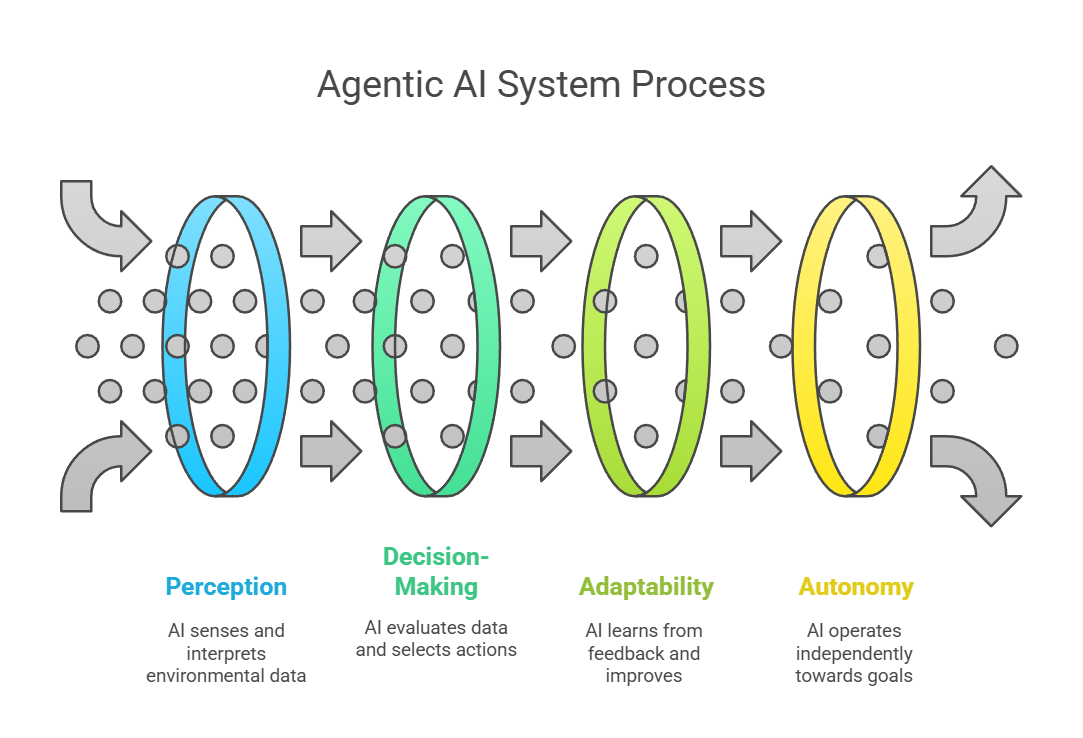
Hierarchy & Relationship: Agents vs. Agentic AI
It’s helpful to view these two concepts as a spectrum:
- AI Agents are the building blocks – the individual specialists.
- Agentic AI is the system that orchestrates these specialists into a cohesive, autonomous unit.
Think of it as a solo musician (AI Agent) versus an entire orchestra conducted by a maestro (Agentic AI). Agentic AI systems coordinate multiple agents to tackle complex, multi-faceted problems that a single agent would struggle with.
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Autonomous Transportation
Waymo vs. Tesla’s Autopilot
- Waymo: Operates as a classic AI Agent with clear parameters. It handles self-driving in controlled environments but still relies on human intervention in unusual scenarios.
- Tesla’s Autopilot: While also an AI Agent, Tesla is progressively integrating more agentic AI features, where the system learns from aggregated data and adapts its driving algorithms over time. Both represent the evolution of autonomy in transportation.
Case Study 2: Customer Service Automation
Traditional AI Chatbots vs. Agentic Support Systems
- Traditional AI Chatbots: Many companies deploy chatbots that answer FAQs based on scripted responses. For example, a telecom company might use a chatbot to help with billing queries.
- Agentic AI Support Systems: A firm like Beta Corp might use an agentic AI system where the initial query is handled by a conversational agent, then multiple sub-agents work to gather data, analyze sentiment, and propose solutions – all while learning from past interactions to improve future responses.
Case Study 3: Financial Trading Platforms
Rule-Based Trading Bots vs. Autonomous Portfolio Managers
- Rule-Based Trading Bots: Some hedge funds use AI agents programmed to execute trades based on specific market conditions. They perform reliably when conditions match predefined scenarios.
- Autonomous Portfolio Managers: Emerging agentic AI systems in finance dynamically adjust investment strategies by analyzing vast amounts of data in real time, anticipating market shifts, and even autonomously executing complex trades – often supervised by risk management sub-agents.
Additional Considerations
Ethical and Operational Oversight
With greater autonomy comes greater responsibility. Businesses must implement robust oversight mechanisms to ensure that agentic AI systems operate within ethical and regulatory boundaries. This might include:
- Human-in-the-Loop Systems: Even highly autonomous systems should have human oversight for high-stakes decisions.
- Audit Trails: Maintaining logs for AI decision-making processes to diagnose issues and ensure accountability.
- Built-in Guards: Mechanisms like internal critics and judges to continuously evaluate and refine AI outputs.
Future Implications
The evolution from AI Agents to Agentic AI is not just a technical upgrade—it signifies a shift in how we interact with technology. As agentic AI systems become more capable, they will:
- Transform industries by automating complex processes.
- Enhance decision-making through dynamic adaptation.
- Raise important discussions on accountability, ethics, and the future role of humans in AI-powered workflows.
Conclusion
In summary, AI Agents are like specialized tools designed to execute well-defined tasks, while Agentic AI represents a more advanced paradigm—one that learns, adapts, and makes autonomous decisions. The real-world examples from transportation, customer service, and finance illustrate the potential of both approaches.
For AI professionals, tech enthusiasts, and business leaders, understanding these differences is key to choosing the right approach for your needs. As the AI landscape evolves, leveraging the strengths of both AI Agents and Agentic AI will be crucial in driving innovation and maintaining ethical standards.
So, the next time you evaluate an AI solution, ask yourself: Am I choosing a smart assistant or an autonomous team member? The answer could very well shape the future of your business.
Feel free to leave your thoughts and comments below – let’s continue the discussion!